Introduction
In a world grappling with environmental concerns and energy needs, the concept of waste-to-energy has emerged as a beacon of hope. This innovative approach addresses two major challenges simultaneously: managing our ever-growing waste problem and producing sustainable energy. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating realm of waste-to-energy, exploring its intricacies, benefits, and potential for a brighter, cleaner future.
Understanding Waste-to-Energy (WtE)
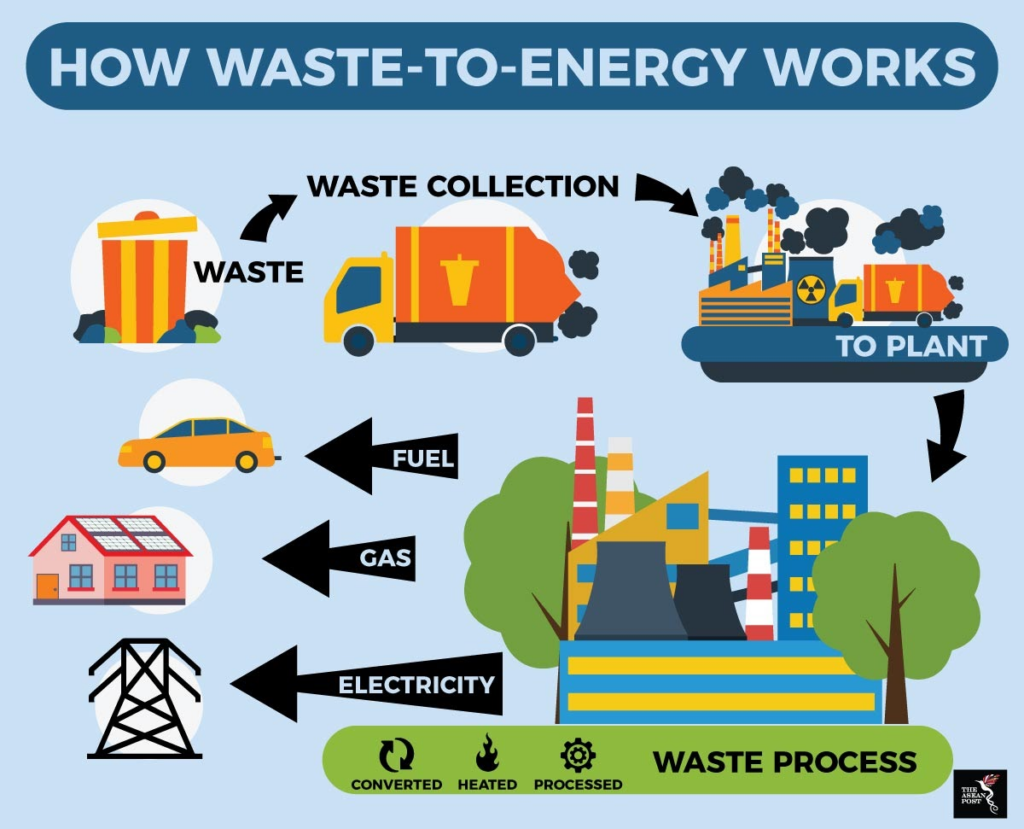
Waste-to-Energy, abbreviated as WtE, is a process that involves the conversion of non-recyclable waste materials into usable energy forms such as electricity, heat, or even fuel. This eco-friendly technology provides an ingenious solution to two pressing issues: reducing landfill waste and meeting energy demands.
The Mechanism Behind WtE
Incineration: A Fiery Transformation
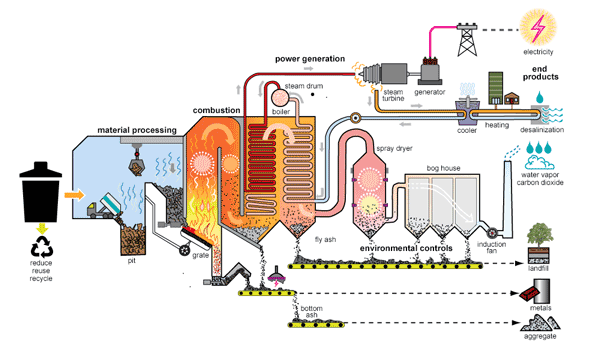
One of the primary methods of WtE is incineration. In this process, non-recyclable waste is burned at extremely high temperatures, generating heat. This heat is then harnessed to produce steam, which drives turbines connected to generators, ultimately producing electricity.
Gasification: Turning Trash into Gas
Gasification is another WtE method. Here, waste materials are converted into a synthetic gas, or syngas, by heating them in an oxygen-deprived environment. The syngas can be further refined and used for electricity generation or as a clean fuel source.
The Environmental Benefits
Mitigating Landfill Problems
One of the most significant advantages of WtE is its ability to reduce the burden on landfills. By converting waste into energy, we can cut down on the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, slowing the depletion of valuable land resources.
Lowering Greenhouse Gas Emissions
WtE facilities are designed to capture harmful emissions and pollutants, significantly reducing their release into the atmosphere. This results in a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to the fight against climate change.
The Economic Advantages
Job Creation
Investing in WtE infrastructure creates job opportunities, from plant operation and maintenance to waste collection and transportation. This not only benefits the environment but also stimulates the local economy.
Energy Independence
By generating energy from our waste, we become less reliant on traditional fossil fuels. This can lead to increased energy security and stability, reducing the impact of energy price fluctuations.
Challenges and Concerns
Pollution Control
While WtE facilities are designed to minimize pollution, challenges in maintaining strict pollution control standards still exist. Adequate measures must be in place to ensure emissions remain within acceptable limits.
Waste Sorting
Effective waste sorting is crucial for WtE processes. Contaminated waste streams can reduce the efficiency of energy production and lead to environmental concerns.
Conclusion
Waste-to-Energy is a promising technology that addresses the dual challenges of waste management and sustainable energy production. By understanding the mechanisms, benefits, and challenges associated with WtE, we can pave the way for a greener and more energy-efficient future.