Introduction
In the intricate symphony of our circulatory system, Factor VIII plays a pivotal role. This unsung hero, also known as Antihemophilic Factor, is crucial for blood clotting. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of Factor VIII, exploring its functions, significance, associated conditions, and the latest research breakthroughs.
What Is Factor VIII?
Factor VIII, or FVIII, is a coagulation factor, a protein that helps the blood clot. It’s one of the essential components in the coagulation cascade, a series of steps that prevent excessive bleeding when we get injured. Without Factor VIII, our bodies would be vulnerable to severe bleeding even from minor wounds.
The Genetics Behind Factor VIII
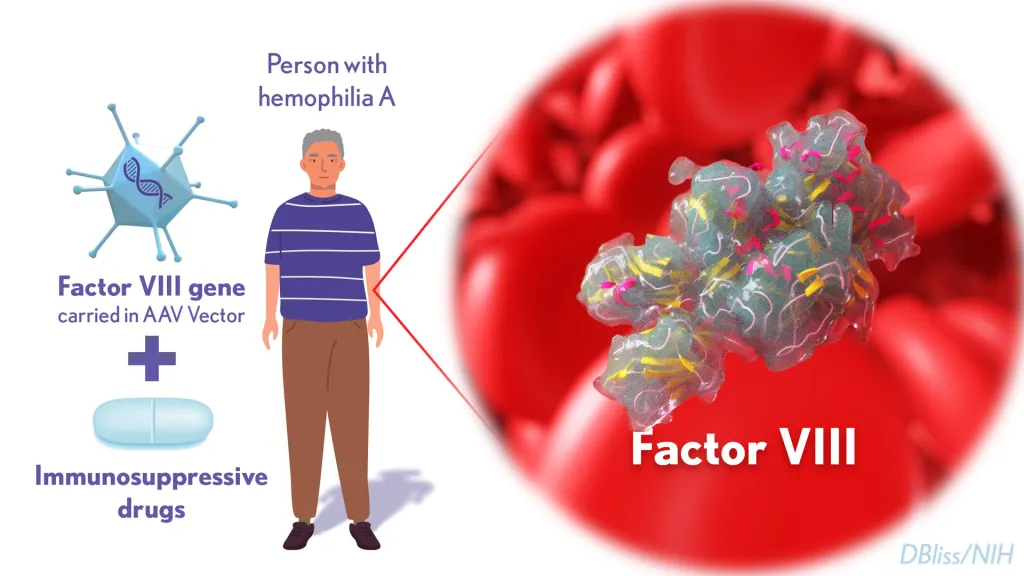
Understanding the genetics of Factor VIII is essential. Hemophilia A, a hereditary bleeding disorder, is often caused by mutations in the F8 gene, leading to insufficient Factor VIII production. This genetic aspect makes Factor VIII a subject of interest in the field of genetics and gene therapy.
The Coagulation Cascade: Factor VIII’s Role
Factor VIII’s primary function is to act as a cofactor for Factor IX. Together, they form a complex that activates Factor X, a crucial step in the coagulation cascade. This cascade ultimately leads to the formation of a stable blood clot, sealing off the injury site.
Hemophilia A: The Factor VIII Deficiency
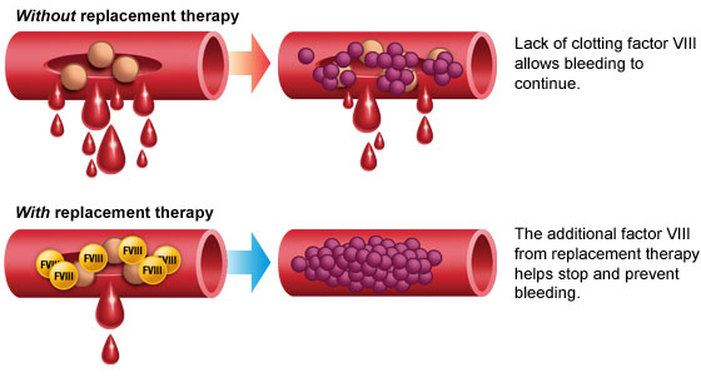
Hemophilia A, the most common form of hemophilia, is characterized by a deficiency or dysfunction of Factor VIII. People with Hemophilia A often experience prolonged bleeding, both externally and internally, which can lead to serious health complications.
Treatment for Hemophilia A
Managing Hemophilia A involves Factor VIII replacement therapy. Patients receive Factor VIII concentrates, either on-demand or as a prophylactic treatment, depending on the severity of their condition. The development of recombinant Factor VIII has revolutionized the treatment, reducing the risk of infections and enhancing patient safety.
Factor VIII and Von Willebrand Factor
Factor VIII’s journey doesn’t end here. It forms a complex with Von Willebrand Factor (VWF), enhancing its stability in the bloodstream. This collaboration is vital for effective blood clotting.
Von Willebrand Disease
Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is a bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of Von Willebrand Factor. Interestingly, VWD can also affect Factor VIII levels in the blood, adding complexity to the diagnosis and treatment.
Research and Innovations
The world of hematology is constantly evolving, and Factor VIII research is no exception. Scientists are continually exploring new therapies and treatment modalities to improve the lives of individuals with bleeding disorders.
Gene Therapy
One promising avenue is gene therapy. Researchers are investigating ways to correct the genetic mutations responsible for Factor VIII deficiencies, potentially offering a lifelong cure for Hemophilia A.
Extended Half-Life Products
To reduce the frequency of Factor VIII infusions, extended half-life products have been developed. These products provide a sustained release of Factor VIII, offering better convenience and quality of life for patients.
Conclusion
Factor VIII, often overshadowed by its more famous counterparts, is undoubtedly a superstar in the world of blood clotting. Understanding its role, especially in conditions like Hemophilia A and Von Willebrand Disease, is crucial for improving the lives of those affected. As research continues to advance, the future looks promising for individuals with Factor VIII-related disorders.