Exploring the Wonders of Polyploidy in Nature
Polyploidy is a captivating genetic phenomenon that has puzzled scientists and intrigued nature enthusiasts for decades. In this comprehensive article, we will dive deep into the world of polyploidy, exploring its definition, types, significance, and its presence in various organisms. Join us on this scientific journey to unravel the mysteries of polyploidy.
Introduction to Polyploidy
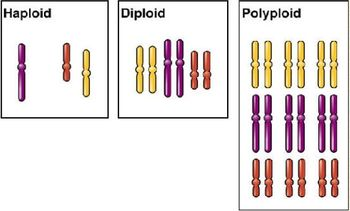
Polyploidy is a genetic condition characterized by having more than two complete sets of chromosomes within a cell or organism. Unlike humans, who are predominantly diploid (having two sets of chromosomes), polyploid organisms possess additional sets, resulting in triploidy, tetraploidy, and beyond.
Types of Polyploidy
- Autopolyploidy: In autopolyploidy, an organism possesses multiple sets of chromosomes from its own species. This can occur due to errors in cell division or through hybridization.
- Allopolyploidy: Allopolyploidy involves the combination of chromosome sets from different species through hybridization, resulting in a new species with a higher chromosome number.
The Significance of Polyploidy
Polyploidy plays a vital role in the evolution and diversity of organisms. Here’s why it’s significant:
- Increased Genetic Variation: Polyploid organisms have a broader genetic pool, enhancing their adaptability to changing environments.
- Hybrid Vigor: Allopolyploids often exhibit increased vigor and vitality compared to their diploid counterparts.
- Crop Improvement: Polyploidy has been harnessed in agriculture to create larger and more resilient crops.
Polyploidy in Plants
Plants are known for their remarkable ability to undergo polyploidy. In fact, many of the plants we encounter daily are polyploids. Some famous examples include:
- Wheat: Hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum) is a staple food worldwide, known for its tolerance to various conditions.
- Bananas: Most edible bananas are triploid, contributing to their unique characteristics.
- Cotton: Polyploid cotton varieties are favored for their fiber production.
Polyploidy in Animals
While less common than in plants, polyploidy does exist in the animal kingdom. Some instances include:
- Amphibians: Some frog species exhibit polyploidy, leading to the development of distinct populations.
- Fish: Polyploidy has been induced in fish species for aquaculture purposes, yielding larger and healthier fish.
- Reptiles: Polyploid reptiles have been identified in certain lizard species, shedding light on their evolutionary history.
Polyploidy in Human Genetics
Although humans are primarily diploid, polyploidy can occur, albeit rarely. It often leads to severe health complications and is incompatible with human life. Understanding these anomalies contributes to our knowledge of genetics.
Conclusion
Polyploidy, with its diverse manifestations across the biological spectrum, continues to be a subject of fascination for scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. Its role in evolution, genetic diversity, and agricultural advancements underscores its significance in the natural world.