Introduction
Electrocardiography, often referred to as ECG or EKG, is a remarkable medical technique that allows us to peek into the intricate electrical signals coursing through the human heart. This diagnostic tool has been invaluable in diagnosing various cardiac conditions, guiding treatment decisions, and improving patient outcomes. In this comprehensive article, we’ll delve deep into the world of electrocardiography, exploring its history, principles, clinical applications, and much more. So, fasten your seatbelts as we embark on this electrifying journey through the heart.
The Birth of Electrocardiography
In the late 19th century, Willem Einthoven, a Dutch physiologist, made a groundbreaking discovery by inventing the first practical electrocardiograph. His invention allowed for the recording of the heart’s electrical activity, forever changing the landscape of cardiology. Einthoven’s work earned him the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1924, solidifying ECG as an indispensable tool in medicine.
Understanding the Basics
How does ECG work?
Electrocardiography involves attaching electrodes to specific points on the body, which then measure the electrical impulses generated by the heart. These impulses, represented as waves on the ECG paper, provide crucial information about the heart’s rhythm and functionality.
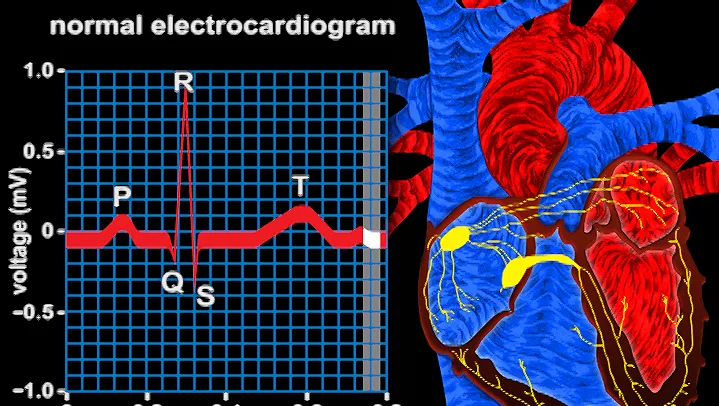
Deciphering the ECG Waveform
The ECG waveform consists of several components, each with its significance. These include the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. Understanding these components is vital in diagnosing various cardiac conditions such as arrhythmias and ischemia.
Clinical Applications
Diagnosing Arrhythmias
One of the primary uses of ECG is the detection and diagnosis of arrhythmias, irregular heart rhythms that can be life-threatening. By analyzing the ECG waveform, healthcare professionals can identify the type and severity of arrhythmias.
Assessing Cardiac Ischemia
ECG plays a crucial role in diagnosing cardiac ischemia, a condition where the heart doesn’t receive enough oxygenated blood. The ST-segment analysis can reveal changes indicative of myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Monitoring Heart Health
Patients with chronic cardiac conditions often require continuous monitoring. Holter monitors and event recorders, both ECG-based devices, are used to track heart activity over extended periods, aiding in long-term management.
The Advancements in ECG Technology
In recent years, ECG technology has witnessed remarkable advancements. The introduction of portable ECG devices and smartphone applications allows individuals to monitor their heart health conveniently. These innovations empower individuals to take charge of their well-being and seek timely medical attention when needed.
ECG in Emergency Medicine
ECG is a cornerstone in emergency medicine, aiding in the rapid assessment of patients with chest pain, palpitations, and shortness of breath. Quick ECG evaluation can mean the difference between life and death in critical situations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electrocardiography stands as a testament to human ingenuity and innovation in the realm of medicine. Its ability to decode the heart’s electrical symphony has saved countless lives and continues to be an essential tool in healthcare. As technology progresses, we can only anticipate more exciting developments in the field of ECG, further improving our understanding of the heart and its complexities.