Introduction
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, staying ahead of the competition is paramount. Traditional manufacturing methods have served us well for centuries, but they have limitations that restrict innovation and cost-effectiveness. Enter additive manufacturing technology, a game-changer that is reshaping industries across the globe.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
Defining the Basics
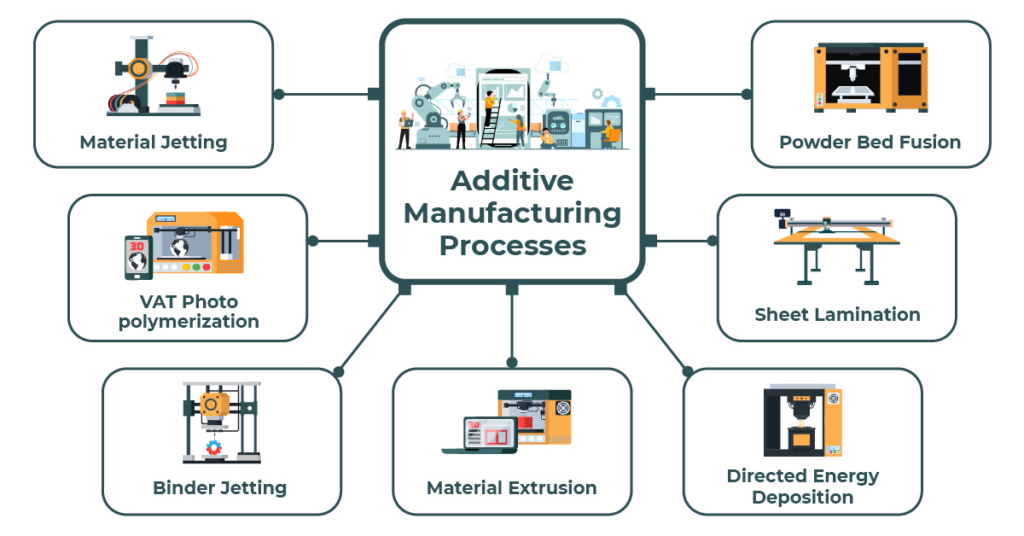
Additive manufacturing, often referred to as 3D printing, is a revolutionary production process that builds objects layer by layer from a digital model. Unlike subtractive manufacturing methods, which involve cutting and shaping materials, additive manufacturing adds material precisely where needed, resulting in minimal waste.
The Key Components
1. 3D Printing Machines
The heart of additive manufacturing, 3D printing machines, are diverse and adaptable. They range from desktop printers for small-scale projects to large industrial machines for aerospace and automotive applications.
2. Digital Design Software
To create 3D-printed objects, you’ll need digital design software. It allows designers and engineers to develop intricate models with precision.
3. Materials
A wide range of materials, from plastics to metals, can be used in additive manufacturing. The choice of material depends on the specific project’s requirements.
Advantages of Additive Manufacturing
1. Design Freedom
With traditional manufacturing, complex designs can be expensive and time-consuming. Additive manufacturing removes these constraints, enabling the creation of intricate and customized products.
2. Rapid Prototyping
Prototyping is a crucial phase in product development. Additive manufacturing accelerates this process, reducing the time it takes to turn concepts into tangible prototypes.
3. Cost Efficiency
Reducing material waste and the need for complex tooling, additive manufacturing can significantly cut production costs.
4. Sustainability
The reduced waste and energy consumption associated with additive manufacturing align with sustainability goals, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Applications Across Industries
1. Aerospace
Additive manufacturing is transforming the aerospace industry. It allows for lighter and more efficient aircraft components, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
2. Healthcare
In the medical field, 3D printing is revolutionizing prosthetics, implants, and even organ transplantation. Custom-made medical devices are improving patient outcomes.
3. Automotive
The automotive industry benefits from additive manufacturing through rapid prototyping and the production of lightweight, fuel-efficient parts.
4. Architecture
Architects are using 3D printing to construct intricate models and even entire buildings, pushing the boundaries of design.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While additive manufacturing offers tremendous benefits, it’s not without challenges. Quality control, intellectual property concerns, and material limitations are some of the hurdles that need addressing.
Despite these challenges, the future of additive manufacturing is promising. As technology advances and becomes more accessible, we can expect to see its widespread adoption across various industries.
Conclusion
Additive manufacturing technology has ushered in a new era of production. Its versatility, cost-efficiency, and sustainability make it a valuable tool for industries seeking innovation. Embracing this transformative technology is not an option but a necessity for those looking to remain competitive in today’s fast-paced world.